From Then Til Now: Kentucky History at A Glance

Before European settlement, diverse Indigenous groups lived and hunted in the region, including the Shawnee, Cherokee, Mingo, Osage, and Chickasaw.

1750
In 1750, Dr. Thomas Walker led the first documented exploration of Kentucky by English colonists, blazing a trail through Cumberland Gap and naming the Cumberland River. His expedition provided early maps and observations that encouraged future settlement and exploration of the region.

1769
In 1769, Daniel Boone climbed Pilot Knob in present-day Powell County, Kentucky, where he possibly first glimpsed the Bluegrass region’s vast wilderness. This moment symbolized the beginning of Boone’s exploration into Kentucky and his role in opening the frontier to westward expansion.
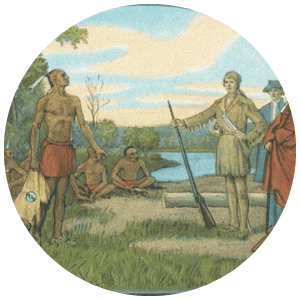
1775
Richard Henderson and Daniel Boone negotiated the Treaty of Sycamore Shoals with the Cherokee people to purchase part of Tennessee and much of Kentucky.

1782
The Battle of Blue Licks was fought along the Licking River on August 19, 1782. It was one of the last major battles of the American Revolution, and it ended in an American defeat.

1792
On June 1, Kentucky is admitted to the union as the 15th state and the first state west of the Appalachian Mountains.

1796

1811-12
New Madrid earthquakes rerouted the Mississippi River and created a small portion of far Western Kentucky not connected to the rest of the state.

1817
The first commercial steamboat route from Louisville to New Orleans opened. The maiden voyage took twenty-five days.

1830
The Louisville and Portland Canal opened, transforming commercial navigation on the Ohio River and contributing to the expansion of the United States' population and commerce.

1830
The third state capitol building opened in Frankfort on Broadway Street.

1836
The Kentucky Historical Society was founded by a group of prominent Kentuckians and was established to preserve the Commonwealth's history.

1850
Louisville & Nashville received a charter from the Commonwealth of Kentucky "...to build a railroad between Louisville, Kentucky, and the Tennessee state line in the direction of Nashville."

1861
On May 16, Kentucky enacts a resolution declaring neutrality in the Civil War, with no allegiance to either the United States or the Confederacy. In September, Kentucky declares full allegiance to the United States, which was in the early months of the Civil War.

1861
In October, Southern sympathizers establish a provisional Confederate government of Kentucky in Bowling Green.
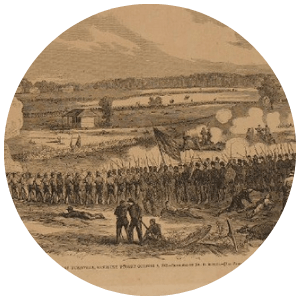
1862
The Battle of Perryville, fought on October 8, 1862, is the largest Civil War battle in Kentucky and marks the climax of the Confederate invasion of the state. Although tactically inconclusive, the Union army's ability to hold the field forces the Confederates to retreat, securing Kentucky for the Union for the remainder of the war.
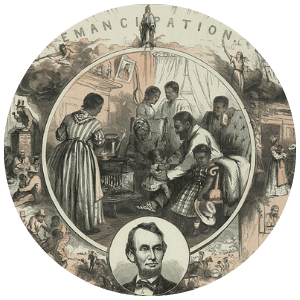
1865
Slavery was legally abolished in Kentucky on December 18, 1865, when the 13th Amendment became part of the Constitution.

1875
The first Kentucky Derby ran at Churchill Downs in Louisville. Aristides won with African-American jockey Oliver Lewis. (Photo courtesy of the Kentucky Derby Museum)

1884
Hillerick & Bradsby, makers of the Louisville Slugger bats, was founded in Louisville. (Photo courtesy of the Louisville Slugger Museum & Factory).

1896
Emma Guy Cromwell became the first woman to hold a statewide office in Kentucky when she was elected state librarian by a vote of the State Senate.

1900
Governor William Goebel died four days after being shot on the morning of January 30 in Frankfort. Gov. Goebel is the only governor in U.S. history to have been assassinated.

1903
The Kentucky Historical Society published the first issue of The Register of the Kentucky Historical Society. It remains the scholarly journal of record for Kentucky history.
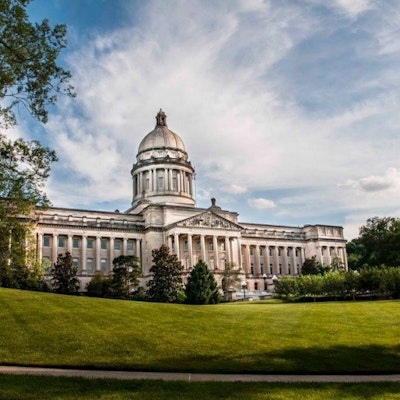

1909
The present Kentucky State Capitol opened in Frankfort.

1920
The 18th Amendment, known as Prohibition, is enacted, leading to significant damage to the state's economy. Prohibition triggers widespread resistance and illegal bootlegging activities.

1926
Mammoth Cave National Park was established.

1933
The New Deal started under President Franklin D. Roosevelt and led to construction and infrastructure improvements throughout the state, including rural electrification.

1937
The United States Bullion Depository at Fort Knox accepted its first gold shipments.

1937
The Ohio River reached its highest level in modern history, driving over one million people from their homes.

1941
Fort Campbell is established; during WWII, it was a training and deployment platform into the European front.

1946
Kentuckian Frederick M. Vinson was sworn in as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He is he only Kentuckian to hold this position.

1954
The Kentucky Historical Society becomes an independent agency of Kentucky state government, but remains a membership organization.

1960
Muhammed Ali (then Cassius M. Clay Jr.) wins a gold medal in the light heavyweight division of boxing at the Olympic Games in Rome.

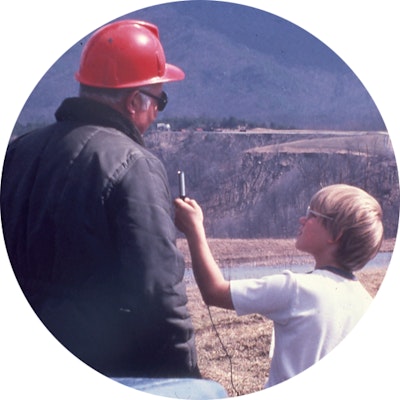
1964
President Lyndon Johnson launched his War on Poverty initiatives from Martin County. Among other things, the War on Poverty created Medicare and Medicaid, expanded Social Security benefits, made the Food Stamp Act permanent, and established the Job Corps, the VISTA program, the federal work-study program, and Head Start. (LB) Library photo by Cecil Stoughton.

1966
Kentucky passed the first statewide comprehensive Civil Rights Act in the South. The act prohibits discrimination in employment and public accommodations based on race, national origin, color, and religion. It also disallows housing discrimination.

1974
Over 20 tornadoes touched down in Kentucky during the April 3-4 Super Outbreak, one of the deadliest and most widespread tornado events in U.S. history. The storms caused widespread destruction across the state, killing 77 Kentuckians and injuring hundreds more.

1976
The Kentucky Oral History Commission was created. It remains the only state agency of its kind in the United States committed to statewide oral history documentation through granting programs and outreach. The Kentucky Historical Society administers KOHC.
1976
Kentucky ratified the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments.

1977
The Beverly Hills Supper Club fire occurred on May 28, 1977, in Southgate, Kentucky, killing 165 people and injuring over 200. It is one of the deadliest nightclub fires in U.S. history and led to significant improvements in fire safety codes and building regulations nationwide.

1983
Martha Layne Collins was elected governor of Kentucky. She is the first woman to hold that office.
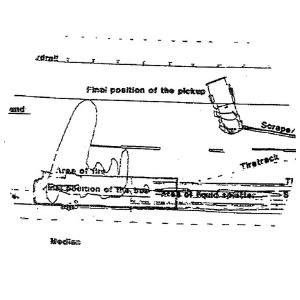
1988
The Carrollton bus crash occurs on May 14, 1988, when a church bus carrying 63 people was struck by a drunk driver in Carrollton, Kentucky, resulting in 27 deaths and 34 injuries, remaining one of the deadliest bus accidents in U.S. history and leading to significant changes in vehicle safety and drunk driving laws.

1999
The Kentucky Historical Society moves into the Kentucky History Center at 100 Broadway St. in Frankfort.

2001
Louisville physicians performed the first implantation of a self-contained artificial heart. The patient, Robert L. Tools, 59, lived 151 days with the device. (Photo courtesy of the University of Louisville).

2005
The Kentucky History Center is renamed Thomas D. Clark Center for Kentucky History in honor of the Kentucky historian laureate, who died at age 102 just before the dedication.

2006
Comair Flight 5191, attempts to take off on the wrong runway at Lexington's Blue Grass Airport on the morning of August 27, 2006, resulting in an overrun and crash that killed 49 of the 50 people on board.

2010
The Kentucky Horse Park in Fayette County hosts the World Equestrian Games, the first time the games had taken place outside of Europe. (Photo courtesy of the Kentucky Horse Park)

2012
Morehead State University and its partners launched the first satellite built entirely in Kentucky. Its 10-year mission was to provide information on the underlying physics of the early universe. A nano-satellite, it was the size of a loaf of bread and weighed five pounds. (Photo courtesy of Morehead State University)

2013
Kentucky legalized the growing of hemp, once an important cash crop for Kentucky for the production of rope and sailcloth.

2020
Kentucky confirms the first state case of the COVID-19 virus on March 6. The pandemic resulted in over 1.6 million confirmed cases and nearly 18,000 deaths in Kentucky by early 2023.

